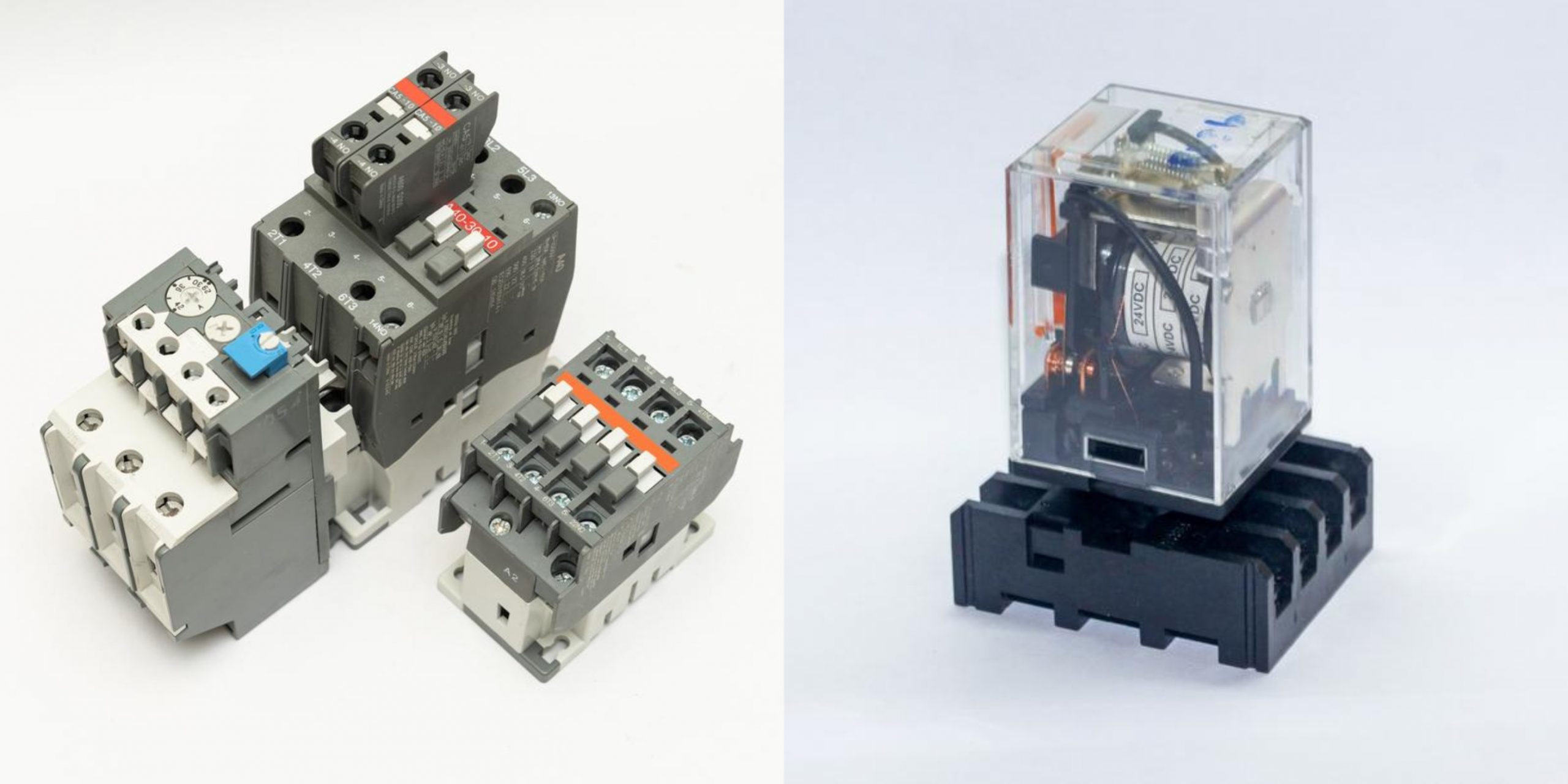
Relays are essential components in various industries, serving as crucial elements in electrical and electronic systems. Their main purpose is to control the flow of current, enabling the efficient and safe operation of complex machinery and systems. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of relays, exploring their main purpose, working principles, and diverse applications across industries.
- Understanding the Main Purpose of a Relay:
Relays act as electromechanical switches, allowing the control of high-power circuits using low-power signals. Their primary function is to isolate and protect sensitive control circuits from the high voltages and currents found in power circuits. By acting as an intermediary between the control and power circuits, relays provide a reliable and safe means of controlling electrical systems. - Working Principles of Relays:
Relays consist of several key components, including an electromagnet, armature, contacts, and a spring. When a low-power signal is applied to the coil of the electromagnet, it generates a magnetic field that attracts the armature, causing the contacts to close or open. This action allows or interrupts the flow of current in the power circuit, depending on the desired control. - Applications of Relays:
3.1 Industrial Automation:
Relays play a vital role in industrial automation, where they are used to control motors, solenoids, valves, and other devices. By utilizing relays, complex processes can be automated, ensuring precise control and enhancing overall system efficiency. Relays also provide overload protection, preventing damage to equipment in case of excessive current flow.
3.2 Automotive Industry:
In the automotive sector, relays are extensively employed for various purposes. They enable the control of lighting systems, power windows, central locking mechanisms, and starter motors. Relays ensure reliable operation and protect sensitive electronic components from high currents, contributing to the overall safety and functionality of vehicles.
3.3 Power Systems:
Relays are indispensable in power systems, facilitating the protection and control of electrical networks. They are used for fault detection, isolation, and restoration, ensuring the stability and reliability of the grid. Relays also enable the coordination of protective devices, minimizing downtime and preventing widespread power outages.
3.4 Telecommunications:
In the telecommunications industry, relays are utilized for signal routing, switching, and amplification. They enable the efficient transmission of data and voice signals across networks, ensuring seamless communication. Relays also provide surge protection, safeguarding sensitive equipment from voltage spikes and electrical disturbances.
Conclusion:
Relays serve as vital components in numerous industries, enabling the control and protection of electrical systems. Their main purpose lies in providing a safe and reliable means of controlling high-power circuits using low-power signals. By understanding the working principles and applications of relays, industries can harness their power to enhance efficiency, safety, and overall system performance.